Low sodium diet — sources, health benefits at NaturalPedia.com
12/15/2017 / By Michelle Simmons

Salt is needed by the body to function properly. Salt contains sodium, which helps the body control many functions. However, too much sodium can be bad and for most people, they get dietary sodium from salt that is in or added to their food. A diet low in sodium typically includes only less than 2,300 milligrams (mg) of sodium a day, while some even limit their sodium intake for 1,500 mg or less per day. A low sodium diet should not include processed foods, such as cured or smoked meats, bacon, hotdogs, sausage, bologna, ham, and salami; anchovies, olives, pickles, sauerkraut, soy sauce, Worcestershire sauce, tomato and other vegetable juices; cheese, bottled salad dressings, salad dressing mixes; and snack foods, such as chips and crackers.

Benefits of low sodium diet
There are several health benefits of low sodium diet. One of these is that it can lower blood pressure. A low sodium diet can be an efficient way to decrease high blood pressure or hypertension. Salt contributes to high blood pressure and less salt intake means less water will be retained. This will help lessen the volume load or strain in the heart and will lower blood pressure. In addition, it may treat resistant high blood pressure.
Another benefit of this type of diet is that it may potentially lower the risks of heart attacks and strokes. If blood pressure is reduced, then the risk for heart attacks and strokes will also decrease. Furthermore, low sodium diet may reduce symptoms of heart failure, kidney failure, or liver failure, such as fluid overload, such as leg swelling, face swelling, and water in the abdomen or lungs. Some studies also suggest that a low-sodium diet may help prevent diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, bloating, osteoporosis, stomach cancer, and asthma.
Food items typically found in low sodium diet
According to an entry by HealthFinder.gov, some of the food items that are typically found in low sodium diet include the following:
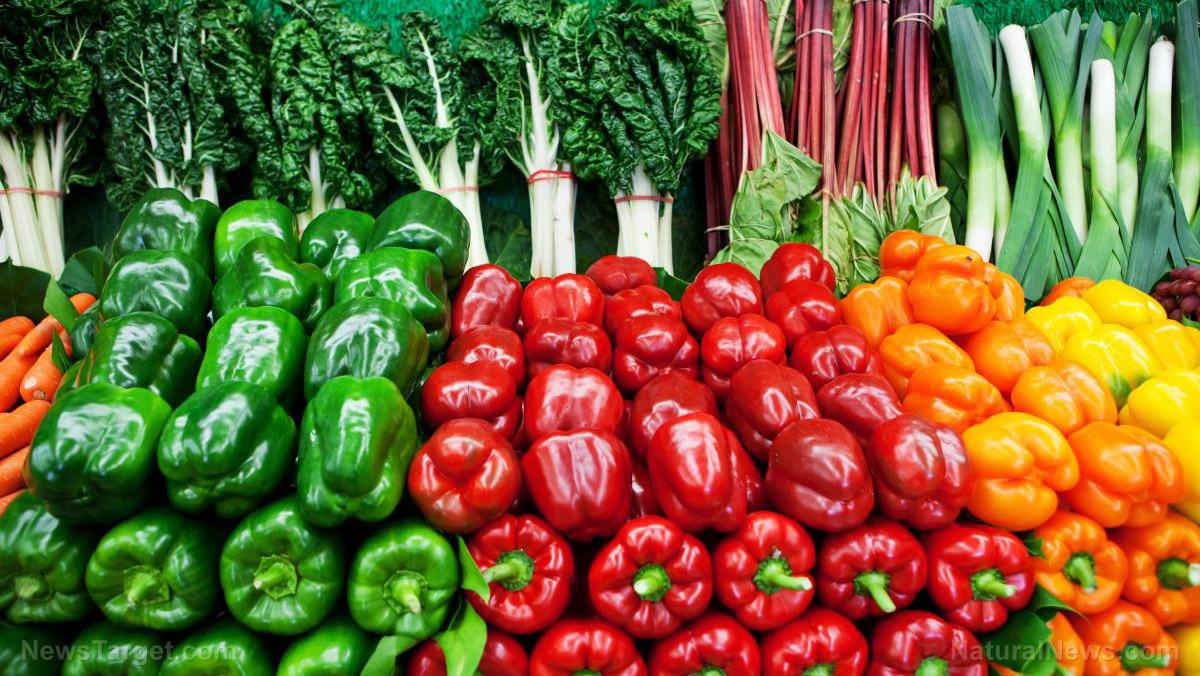
- Fresh fruits, such as apples, oranges, or bananas
- Fresh vegetables, such as spinach, carrots, or broccoli
- Frozen vegetables without added sauce
- Canned vegetables that are low in sodium or have no salt added
- Low sodium vegetable juice
- Unsweetened frozen or dried fruit
- Canned fruit packed in water or 100 percent juice and not syrup
- Rice or pasta
- Unsweetened oatmeal
- Unsalted popcorn
- Fish or shellfish
- Chicken or turkey breast without skin
- Lean cuts of beef or pork
- Unsalted nuts and seeds
- Dried peas and beans
- Canned beans labeled “no salt added” or “low sodium”
- Eggs
- Dairy products, such as fat-free or low-fat milk and yogurt, low- or reduced-sodium cheese, soymilk with added calcium
- Dressings, oils, and condiments, such as unsalted margarine and spreads with no trans fats; vegetable oils, such as canola, olive, peanut, or sesame; sodium-free, light mayonnaise and salad dressing; low-sodium or “no salt added” ketchup; and vinegar
- Seasonings, such as herbs, spices, or salt-free seasoning blends; chopped vegetables, like garlic, onions, and peppers; lemons and limes; and ginger
Body systems supported by low sodium diet
The body systems supported by low sodium diet include the cardiovascular, digestive, nervous, respiratory, and skeletal systems.
Where to learn more
- Top Foods to Avoid with High Blood Pressure
- Restricting your sodium intake does NOT reduce your blood pressure, researchers find
- Low salt diet does not reduce heart disease, study finds
- Low salt diets don’t work and hurt your body
- Low-salt diets increase risk of stroke and heart disease, study says
Summary
A low sodium diet typically includes only less than 2,300 mg of sodium a day. Some people even limit their sodium intake for 1,500 mg or less per day.
Low sodium diet may lower blood pressure and may treat resistant high blood pressure.
Low sodium diet may lower the risks of heart attacks and strokes.
Low sodium diet may reduce symptoms of heart failure, kidney failure, or liver failure.
Low sodium diet may help prevent diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, bloating, osteoporosis, stomach cancer, and asthma.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Low sodium diet